What Is Sanger Sequencing? A Technical Breakdown of the Process
Sanger sequencing is a technique used in molecular biology and genetics to
sequence the DNA or RNA of a particular organism. It is also known as Sanger
DNA sequencing or simply Sanger sequencing. The process has been used for
several decades now and is one of the most common methods for sequencing DNA.
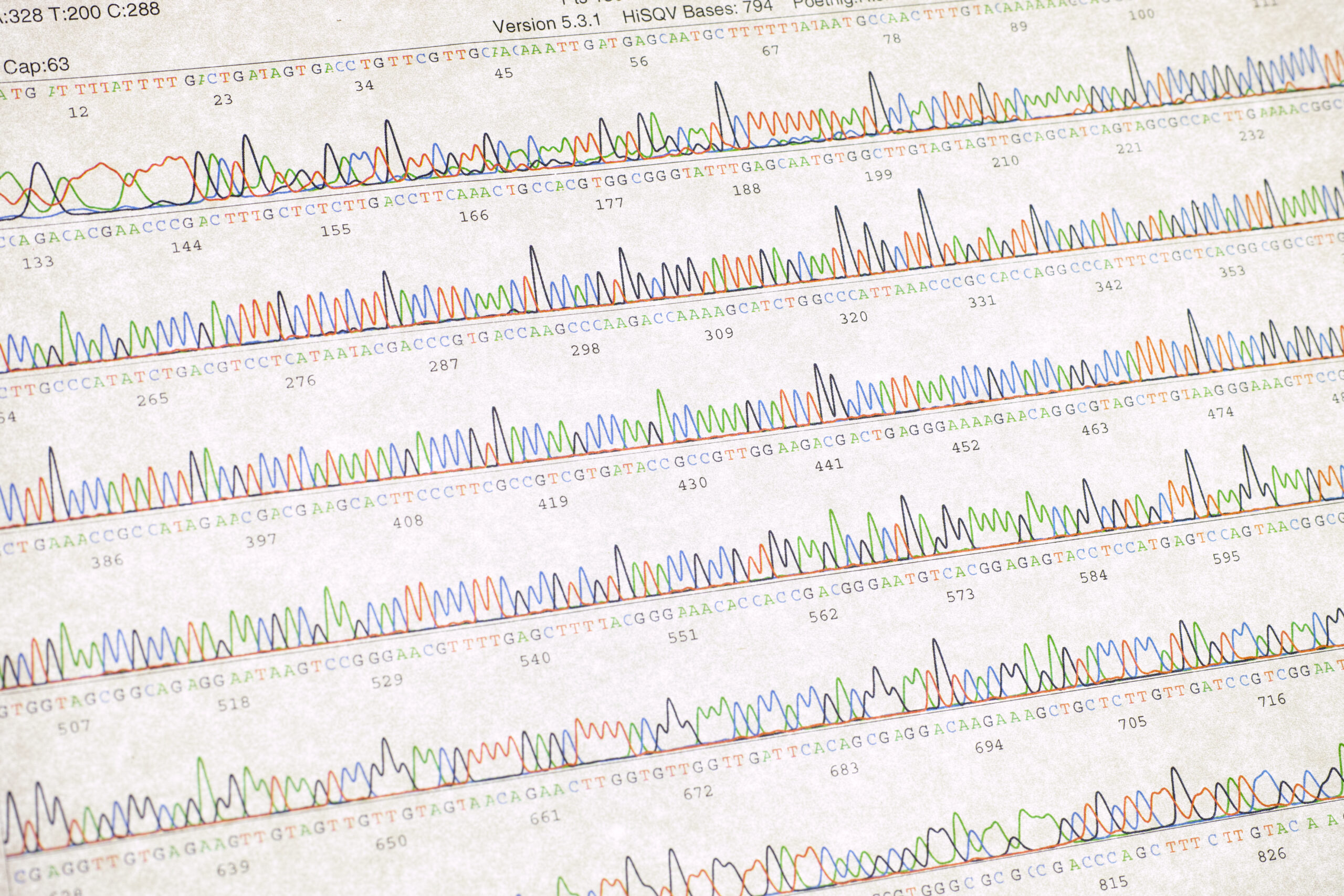
What Is Sanger Sequencing?
Sanger sequencing is a technique used to determine a specific sequence of DNA.
The name of the method is mostly derived from its inventor, Bryan D. Sanger.
The method was first introduced in 1979, though it was first used in a
laboratory in 1974. The idea behind Sanger sequencing is simple: a DNA molecule
is cut into small pieces and then bound to a specific molecule. This is done
with the use of a piece of restriction enzymes that can cut DNA. Once the DNA
is cut into small pieces, it is then attached to fluorescent dye molecules. The
DNA is then introduced into a gel, which is then stained with a fluorescent
molecule. Through this process, the DNA molecules that were bound to the
fluorescent molecules can be detected on the gel. After this, the DNA is
isolated from the gel and then used to sequence the genome by running it
through a machine that is able to read the DNA.
How Is Sequencing Made?
There are two ways to perform Sanger sequencing. One is called enzymatic
sequencing, where DNA is enzymatically cleaved into smaller pieces. The other
is called pyrosequencing, where DNA is burned into nanoparticles and then
sequenced by an optical method. Each method has its pros and cons, so a
researcher must decide which method is most suitable for the research being
conducted.
Why Is Sanger Sequencing Used?
There are several reasons why this sequencing is used. First of all, it can be
used to determine the specific sequence of DNA. This is a very important step
in many different fields of research, as it allows doctors and researchers to
identify mutations within the genome. It can also be used to determine the
location of particular DNA sequences within a genome.
Another reason why this sequencing method is used is because it is a relatively
simple method. This is important, as researchers can use it to sequence short
stretches of DNA, such as single nucleotides, known as DNA oligonucleotides. It
is also important to note that single nucleotide polymorphisms are very easy to
detect. This means that they are easy to detect with Sanger sequencing.
אין תגובות:
הוסף רשומת תגובה